Modern Compressed Air Pipe Systems
 The purpose of the compressed air piping system is to deliver compressed air, efficiently, to the points of use. Compressed air needs to be delivered with the right volume, appropriate quality as well as pressure, to properly power the components that use compressed air.
The purpose of the compressed air piping system is to deliver compressed air, efficiently, to the points of use. Compressed air needs to be delivered with the right volume, appropriate quality as well as pressure, to properly power the components that use compressed air.
Compressed air is costly to manufacture. A poorly designed compressed air system can increase energy costs, promote equipment failure, reduce production efficiencies, and increase maintenance requirements.
It is generally considered true that any additional costs spent improving the compressed air piping system will pay for itself many times over the life of the system. Compressed air is utilized in many commercial industrial facilities and is considered a utility that is essential to production. AirPro’s aluminum compressed air pipe system provides airtight fittings with full bore flow creating a more energy efficient system.
Aluminium compressed air pipe systems are quick to install and ready for immediate pressurization. Components are removable and interchangeable and allow immediate and easy layout modifications reducing production downtime. Unlike the performance of steel pipe, which degrades over time due to corrosion, air quality is clean with optimum flow rate performance with the use of a Aluminium pipe system.
Thanks to its large choice of sizes in 100mm (4″), 76mm (3″), 63mm (2 1/2″) , 40mm (1 1/2″), 25mm (1″), 16.5mm (1/2″) and an extensive range of accessories, the Airpro system meets the requirements of numerous industrial and garage workshop installations. Furthermore, you can’t beat the simple installation, energy savings, and layout flexibility of AirPro compressed air piping solutions.
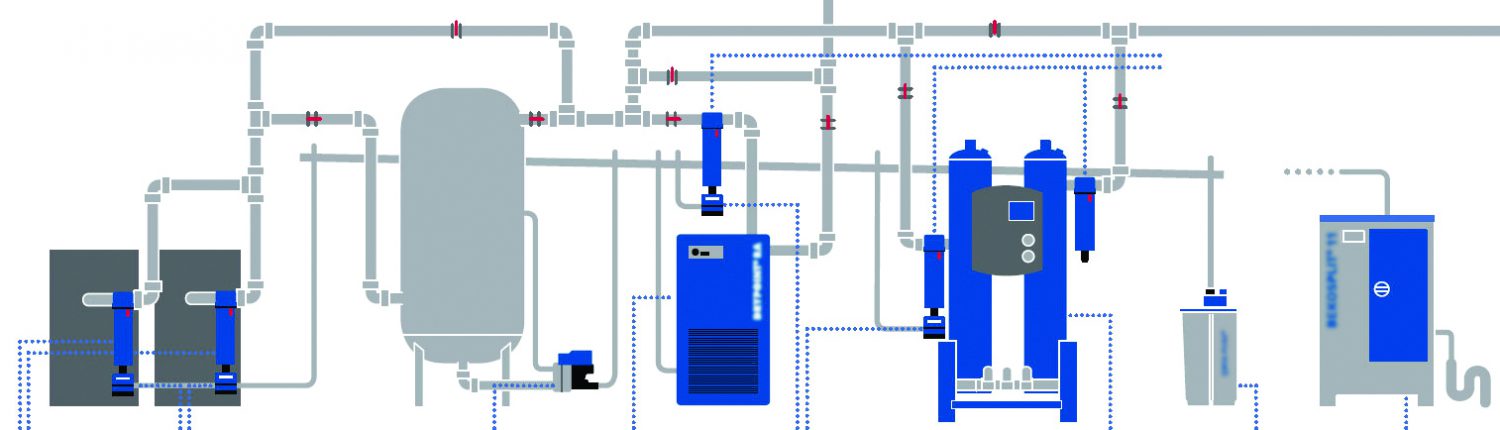
Example of a Compressed Air Pipe System
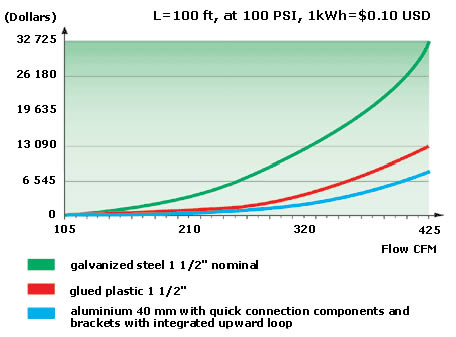
Controlling Operating Cost
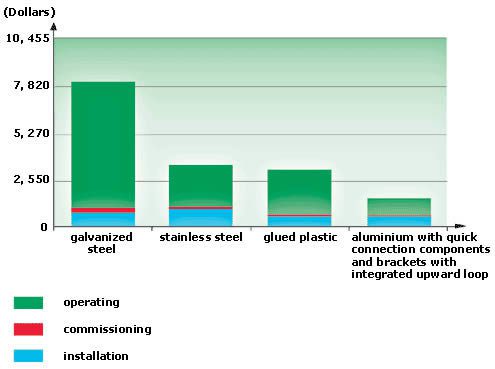
Cost of pressure drops over a 10-year period:
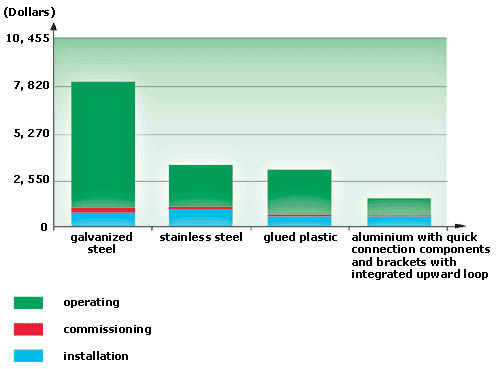
Annual costs: In terms of overall performance versus costs, the choice should not only depend on technology and purchasing price. The exact cost of a system also includes annual operating costs (such as installation and commissioning of a system.
Example of Annual Costs for a 200m system:
Operating: addition of drops, pressure drop, leaks, maintenance
Commissioning: leak detection, painting
Installation: materials, labor